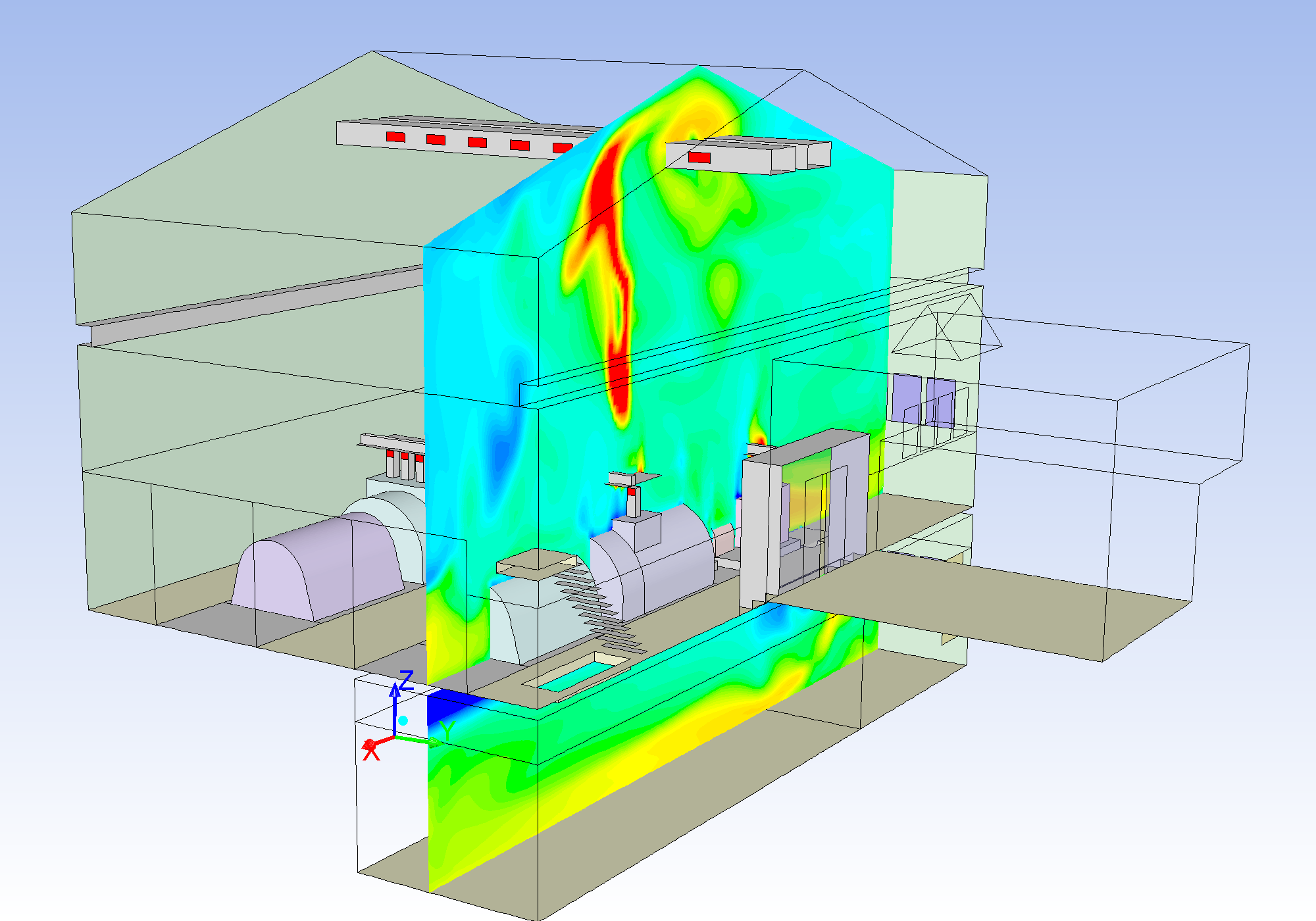
CFD Simulation
The calculation and representation of flows within rooms or arbitrarily shaped objects, taking into account all relevant physical influencing factors.
CFD simulation: non technical functional term, feminine [the].
CFD stands for Computational Fluid Dynamics.
CFD simulation enables the calculation and representation of flows within any geometries, e.g. recreation and production rooms, including all physical parameters (e.g. velocities, temperatures, pressures, as well as concentrations of gaseous substances or particles, particle trajectories, comfort parameters) with great accuracy. Both Stationary (constant over time) as well as and transient (variable over time) processes can be considered.
What is CFD simulation used for?
CFD simulation is a frequently used, extremely helpful tool for the investigation, the development and the optimisation of nearly all types of flow processes. In the field of ventilation technology, CFD simulation can sustainably support the development and optimisation of ventilation components and concepts.
The many possibilities of a CFD simulation explained interactively:
Data flexibility – further possibilities offered by CFD simulation
In addition to the possibilities shown, CFD simulation can also provide effective support for the following topics, both for existing and planned or fictitious (model) facilities or premises:
- Visualises the spread of bacteria and viruses in rooms.
- Shows the spread of pollutants in rooms, in buildings or outdoors
- Enables the analysis of the thermal situation inside a building
- Facilitates the analysis of the airflow situation in rooms or buildings (e.g. draughts)
- Illustrates the comfort situation in rooms, etc.
How does CFD simulation work?
A CFD simulation is developed and created in four consecutive steps.
Step 1
Step 1
A simulation model is created of exactly the flow area that is to be investigated in detail. As a basis for this, existing 3D CAD data of the object can be directly transferred and processed.
Step 2
Step 2
This is followed by the subdivision of the model into the smallest calculation units, the so-called cells. This step is also called “meshing”. The complexity of the simulation model results from the size and the required level of detail. The number of cells can range from a few thousand to several tens of millions.
Step 3
Step 3
The entire model is parameterised; this is followed by the actual calculation.
Step 4
Step 4
In the fourth and last step, the evaluation and the illustrative presentation/visualisation of the calculated results take place.
Advantages of CFD simulation
Minimise costs in advance
With a CFD simulation, cost-intensive measurements can be either usefully supplemented in advance during the planning of plants or reduced to a minimum or in some cases even completely replaced
Full control over all boundary conditions
In a simulation, all boundary conditions, especially the thermal boundary conditions (weather), can be completely controlled. This makes it possible to reproducibly compare different solution approaches in the model under exactly definable boundary conditions.
Review existing solutions
Thanks to a CFD simulation, existing tasks in the ACTUAL state and associated solution approaches can be mapped, checked and optimised in detail.
Avoid bad investments
By means of a professionally supervised CFD simulation, planned systems can be checked with regard to their functions and modes of operation even before realisation. This means that bad investments can be avoided and new systems can be optimally adapted to the actual requirements.
Energy saving through fluidic optimisation
With a CFD simulation, components can be optimised in terms of flow. In many cases, this leads to relevant energy savings.
Limitations of CFD simulation
Optimisation through experience
The CFD simulation can show ACTUAL states and provides important findings already in the planning phase of ventilation components and systems. However, this tool cannot automatically suggest optimisation measures. This requires expert advice and many years of experience in order to convert the results into practicable solutions.
Reality vs. simulation
Although CFD simulation software has made very great progress over the last 20 years, there are still some highly complex processes (e.g. production and machining processes) that cannot be directly represented in a simulation model. Nevertheless, with well-founded, plausible assumptions, very good solution concepts can be developed.
Limits of complexity
A CFD simulation is based on an intensive calculation process. The more complex the requirements, the longer the calculation times. However, due to continuously improved hardware and software, these limits are constantly expanding.
What we offer you
With a CFD simulation, you can check the effect of changes (e.g. different concepts) and the influence of changed boundary conditions (e.g. changed temperatures or climates) and optimise functionality as well as energy efficiency (virtual prototyping) even before the (re)construction of buildings, plants or components.
Your investments are thereby optimised economically and ecologically and thus sustainably secured.
We offer you extensive expertise. We have now been active for over 25 years in the field of process ventilation as well as in the field of general heating, ventilation and air-conditioning technology and have been using the CFD simulation tool on a larger scale for over 15 years.