Extract Air & Process Air
SB nozzle plate (type DPL)
- Design as flat plate surface with suction nozzle(s)
- Efficient replacement of conventional capture bonnets (funnel / box-shaped)
- Stabilised capture of emissions from point sources, even with cross-flows
- Simple, versatile modifiable and adaptable design
- Smallest possible mounting distance to the emission source
- Particularly large depth effect with a high degree of quality
- Minimised capture air flow due to high pollutant capture efficiency
- Smaller separation systems, thus reduction of operating costs
- Less susceptibility to contamination
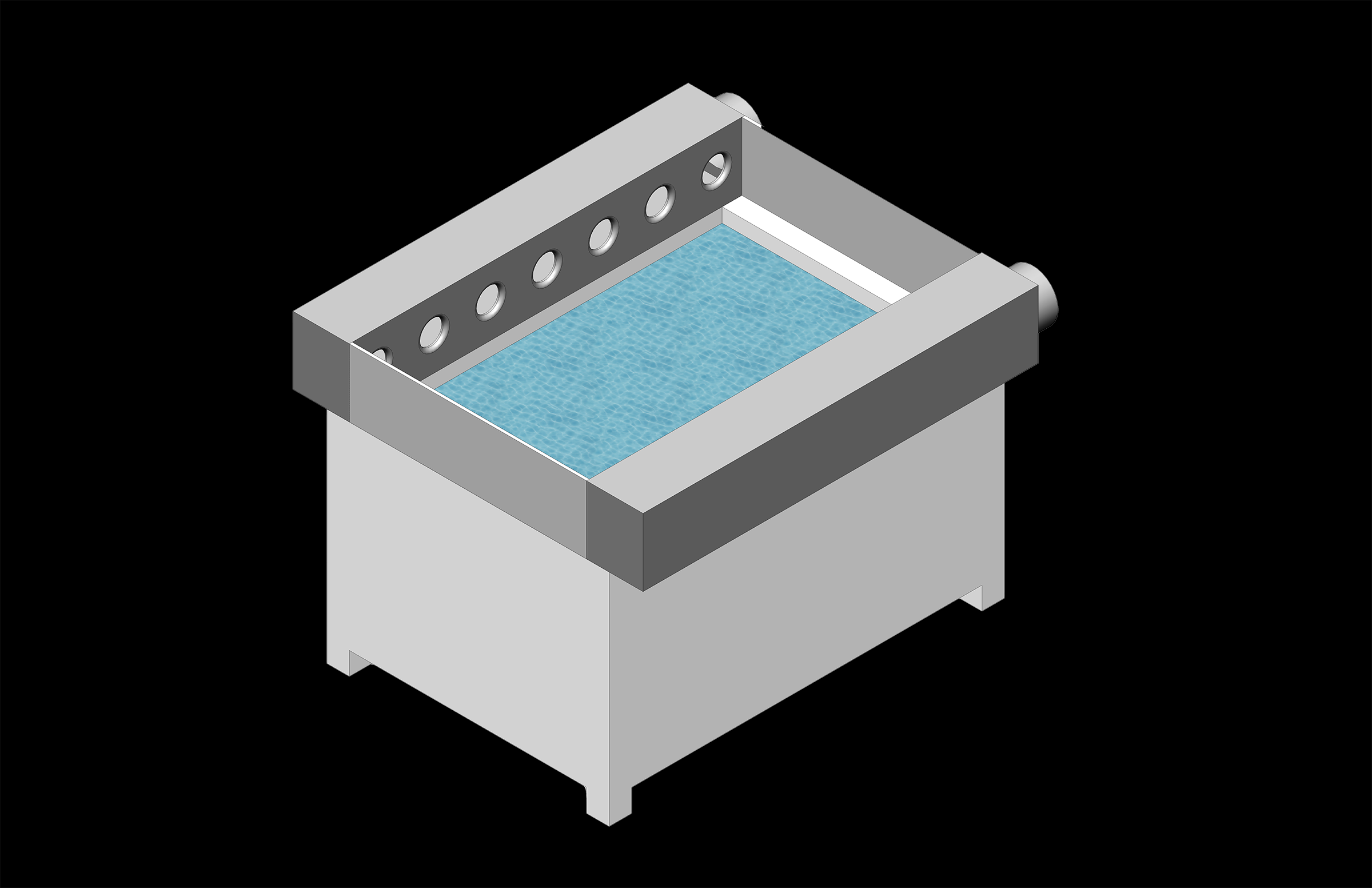
SB bath rim suction unit (type BRA)
- Design as vacuum element with suction nozzles in linear arrangement
- Efficient replacement of conventional slot capture systems
- Stabilised capture of emissions from area sources
- Optimum free access to the process plant from above
- Particularly large depth effect with a high degree of quality
- Minimised capture air flow due to high pollutant capture efficiency
- Smaller separation systems, thus reduction of operating costs
- Less susceptibility to contamination
SB vortex extraction (type WAS)
- Design as a contour element with superimposed negative pressure fields
- Versatile use, especially for impulsive and thermally superimposed emissions with longitudinally expanded source
- Stagnation point-free capture of emissions from linear emission sources with a high degree of quality
- Generation of an artificial “whirlwind / typhoon“
- Peripheral velocities in the rotating field up to 70 m/s
- Negative pressure in the centre above 1,000 Pa
- Minimised capture air flow due to high pollutant capture efficiendy
- Smaller separation systems, thus reducing operating costs
- Optimal access to the emission sources from above (with hinged design)
SB-Jetline (Type JET)
- Design as a combination of nozzle and vortex capture devices
- Versatile use, especially for pulsed and thermally superimposed emissions with longitudinally expanded source
- Stagnation point-free capture of emission from linear sources with a high degree of quality
- Minimised capture air flow due to high pollutant capture efficiency
- Smaller separation systems, thus reducing operating/energy costs
- Optimal access to the emission sources from above (with hinged design)
Example applications from practice
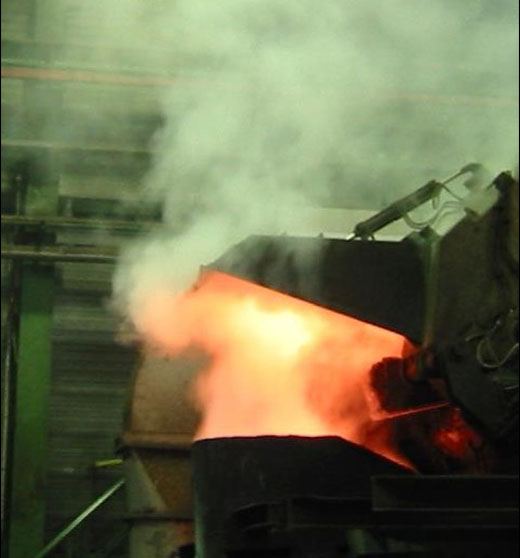
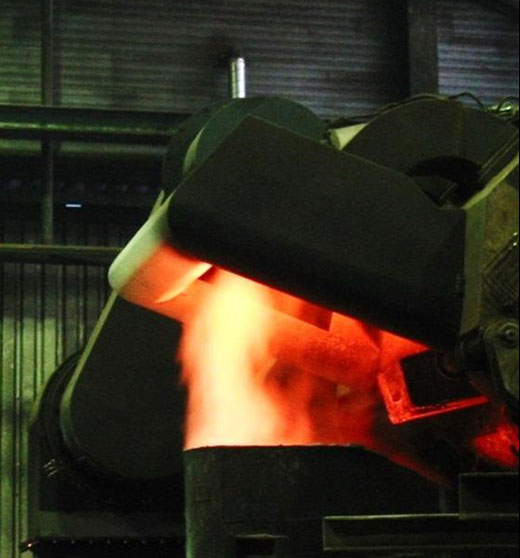


Optimised emission capturing using a self-service vortex extractor (type WAS)
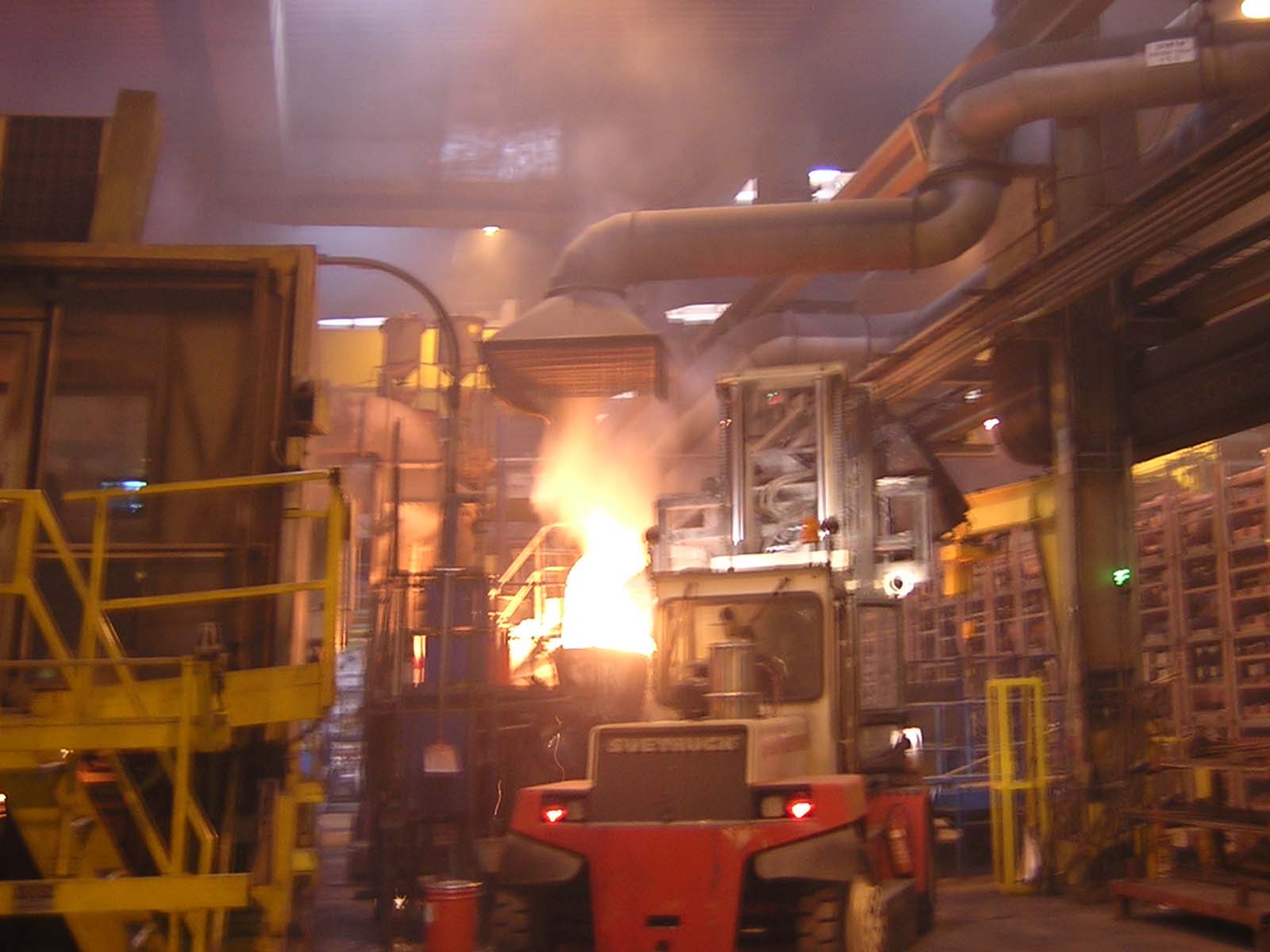
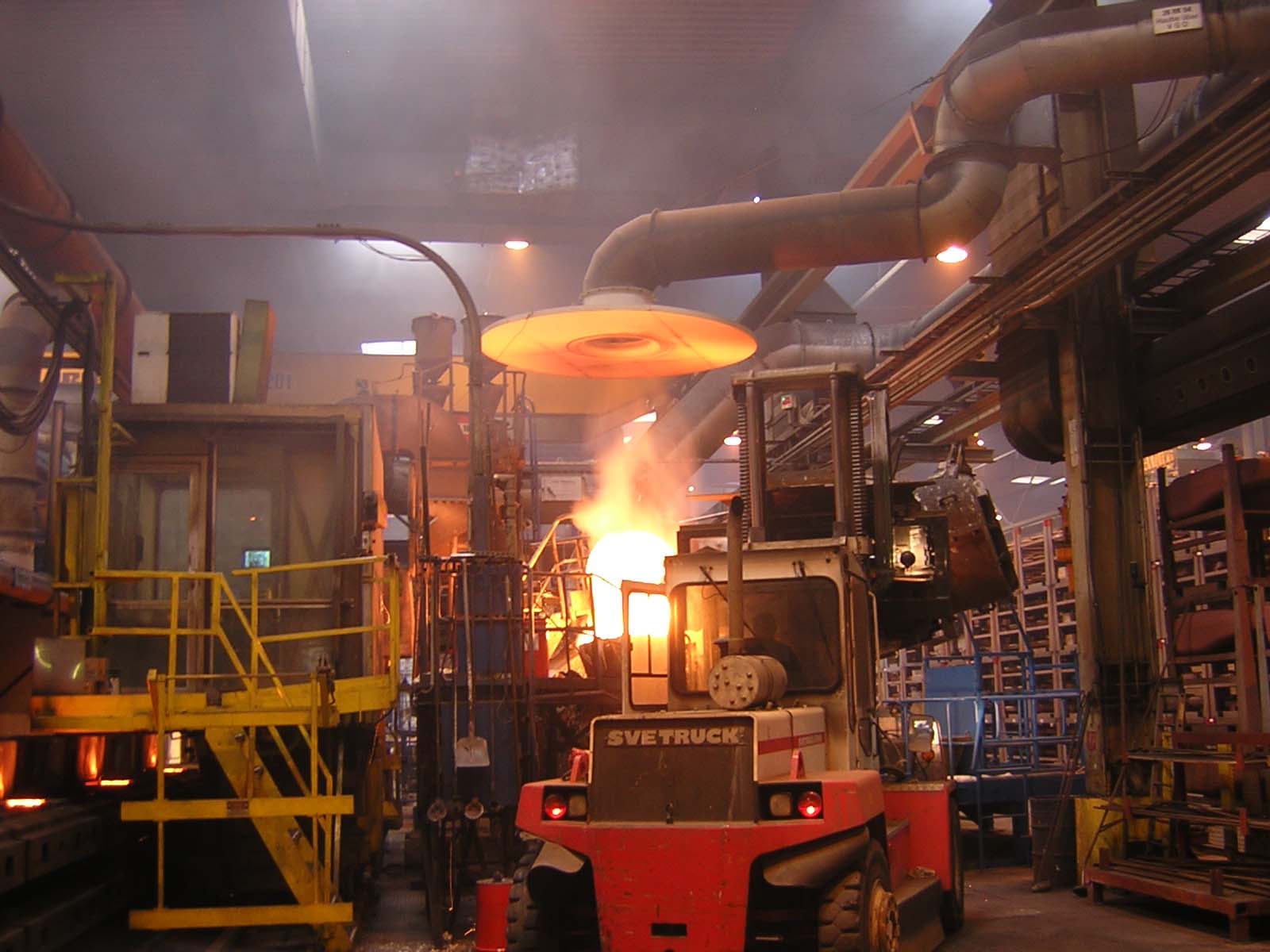


Optimised emission capturing using a SB nozzle plate (type DPL)
